Vitamin D & Calcium Deficiency: What You Need to Know
Learn how these essential nutrients work together to support your health, and what happens when you're deficient in either.
Introduction
Vitamin D is synthesized in the skin through sunlight exposure and is also available in foods and supplements. It helps the body absorb calcium, promote bone and muscle health, and support immune function.
Calcium, found in dairy, leafy greens, and fortified foods, is vital for strong bones and teeth and regulates muscle contractions.

Are Vitamin D and Calcium Deficiencies Linked?
Yes! Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium from the small intestine. Without enough vitamin D, even high calcium intake might not be effective, leading to bone issues and muscle weakness.
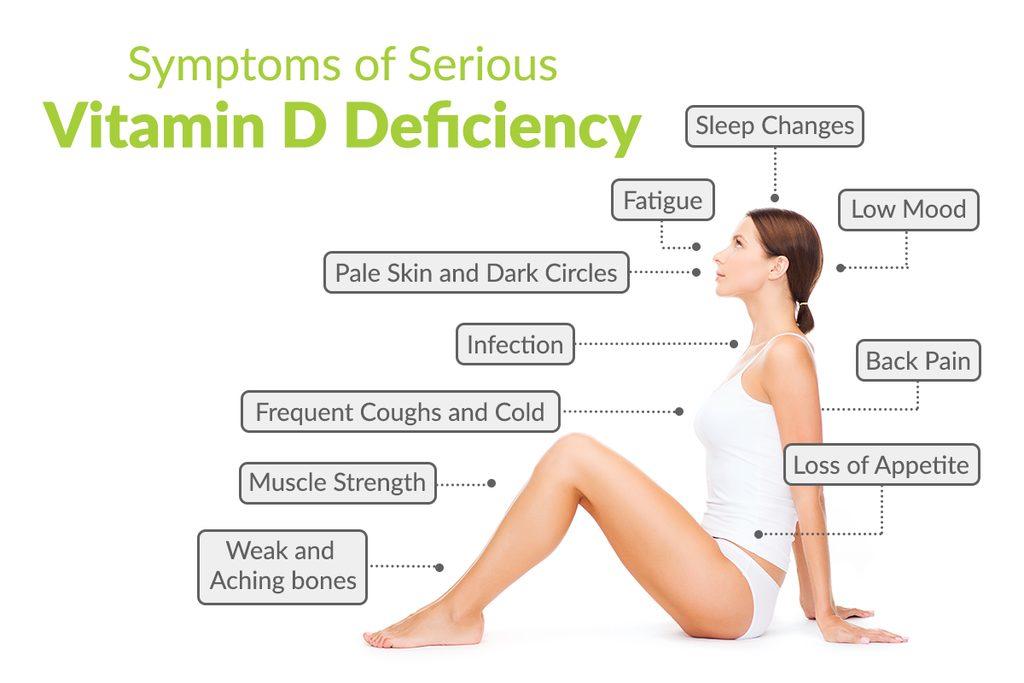
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Fatigue: Often overlooked, low vitamin D can cause chronic tiredness.
- Hair Loss: Linked to alopecia and poor hair follicle health.
- Mood Swings & Depression: Can contribute to mental health issues including anxiety and depression.
- Weak Bones: Increases risk of fractures and conditions like osteoporosis.
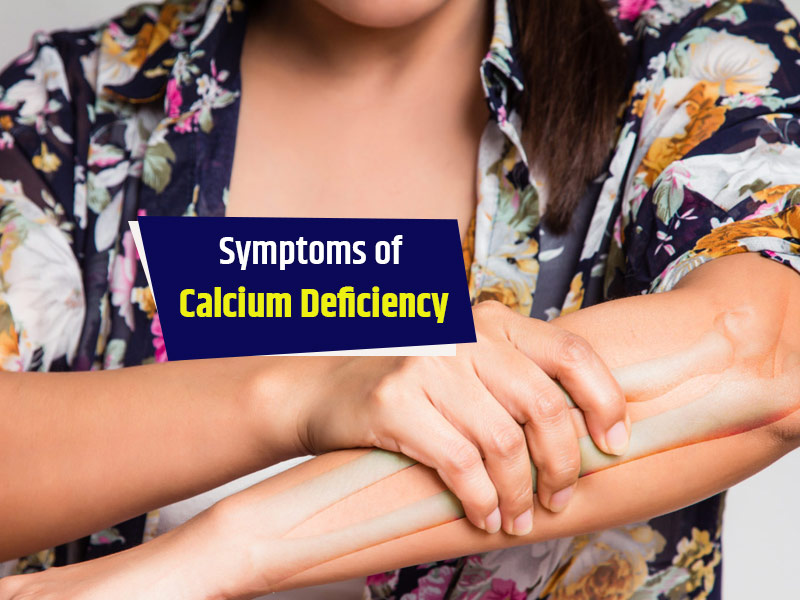
Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency
- Muscle Cramps: Painful spasms due to low calcium.
- Hallucinations: Severe deficiency can affect mental function.
- Brittle Nails: Thin, weak nails often signal calcium deficiency.
- Severe PMS: Women may experience worse symptoms before menstruation.
Top Sources of Vitamin D and Calcium
Vitamin D-Rich Foods:
- Fatty fish like salmon
- Fortified milk and cereals
- Egg yolks
- Sunlight
Calcium-Rich Foods:
- Dairy (milk, cheese, yogurt)
- Leafy greens like kale, spinach
- Fortified soy/almond milk
- Tofu, sesame seeds, and almonds

How to Maintain Healthy Levels
- Expose yourself to sunlight safely for at least 10-30 minutes a few times a week.
- Include Vitamin D and Calcium-rich foods in your diet daily.
- Consider supplements if you're not meeting the daily recommended intake.
- Get regular health check-ups and talk to your doctor about your vitamin levels.